Template Assisted Synthesis of Magnetic Wireless Nano-Agents
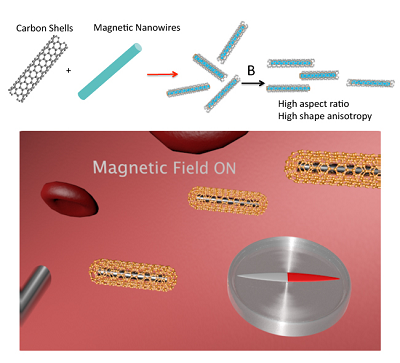
Shrinking devices to the nanoscale creates a wealth of new possibilities in nanomedicine, such as targeted drug delivery platforms. While the futuristic vision of nanovehicles capable of reaching and exploring inaccessible tissue within the human body is compelling, combining propulsion, targeting and controlled drug release in vivo remains a challenge. The design of a biomedical nanoplatform for targeted drug delivery entails significant challenges including the transport and control of the nanostructure. The use of magnetic fields to wirelessly manipulate small magnetic therapeutic agents is attractive since it has the potential to allow them to be driven to confined spaces in the human body. While magnetic nanoparticles have been well studied for use as drug carriers, other structures such as nanowires (NWs) can provide advantages, primarily because their shape anisotropy facilitates magnetic actuation.
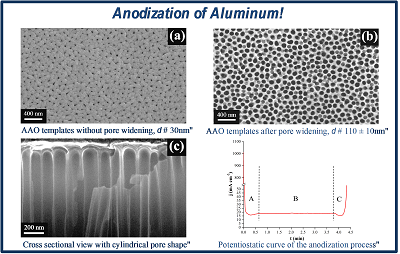
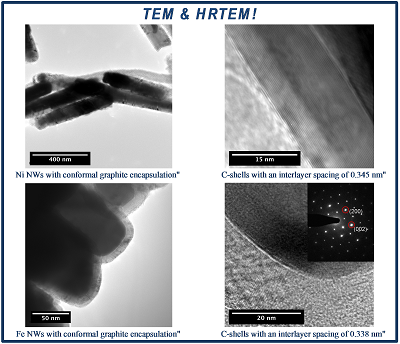
We carry out research in batch fabricating hybrid nanostructures consisting of magnetic NWs encapsulated by graphitic shells using template-assisted chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The resulting hybrid structures display uniform and high quality graphitic coatings. Graphitic encapsulation of NWs works twofold: (1) Protects the core from oxidation, (2) Allows further functionalization such as attachment of chemotherapeutic drugs or fluorescent dyes.